Luminnova P3 Protocol: PDT | PBM | Postbiotics to Boost Innate Immunity
Luminnova Health proposes leveraging the power of PDT, PBM and postbiotics to optimize innate immune defense. In abbreviated form we refer to it as the P3 protocol.
THE IMPORTANCE OF THE INNATE IMMUNE SYSTEM IN CoVID-19 DEFENSE
The innate immune system plays a crucial role in defending against infections. With respect to COVID-19, influenza, and other infections it serves as the body's first line of defense, providing rapid responses to invading pathogens. It is usually robust in young children but becomes less responsive with advancing age or with poor health.
The concept of "training" the innate immune system refers to a process whereby innate immune cells actually become reprogrammed after initial encounter with an infectious agent in a way that makes it better prepared to respond to a similar infection in future. This is the reason why adults don’t get as many colds as children despite the fact that children actually have a more robust functioning innate system. It’s also the reason why adults had much more severe CoVID-19 symptoms compared to children as no one had been exposed to this type of virus before and therefore there was no opportunity to train the innate response prior to exposure. In this case children had a distinct advantage due to their naturally robust innate immunity, which underscores the importance of a well functioning innate immune system.
In many cases a healthy innate immune system can respond to and eliminate infections on its own. However if the innate system is overwhelmed, for example, by a high viral load, the more specific adaptive immune system is then engaged. The adaptive system employs antibodies and other mechanisms which are targeted at specific antigens such as the spike protein.
A robust, perfectly matched antibody response is very effective at destroying viruses and in turn has negative feedback on the innate system, presumably to avoid an excessive response.
CHALLENGES ENCOUNTERED
Vaccination and severe CoVID-19 infection can program the adaptive immune system to respond predominantly to the original CoVID-19 Wuhan strain even when new strains are encountered thereafter. This is a well recognized phenomenon referred to as immune imprinting.
Source: N. Lasrado et al. Antibodies directed at Wuhan strain 25,954 compared to 59 directed at XBB.1.6 three weeks after bivalent booster. Month 3: 21,804 against wuhan strain and 70 against XBB.1.6
The challenge is that there have been a rapidly emerging series of new variants with a large number of mutations in the spike protein. As a result, the antibodies no longer fits into the lock and key socket on the spike protein and the virus is not properly neutralized. This presents a further problem because the mismatched (sub-optimal) antibody response can still dampen the innate immune response and reduce the ongoing training of this system to quickly recognize and deal with the circulating viruses as each new variant appears. Exposure to the virus prior to vaccination lessens the risk of immune imprinting, unless there was severe infection.
Another recognized challenge is a phenomenon referred to as antibody dependent enhancement of infection (ADEI) which has been previously described in the context of other types of vaccination, for example, dengue fever and other coronaviruses. In this case the antibodies interact with the virus in a way which actually promotes entry of the virus into our cells.
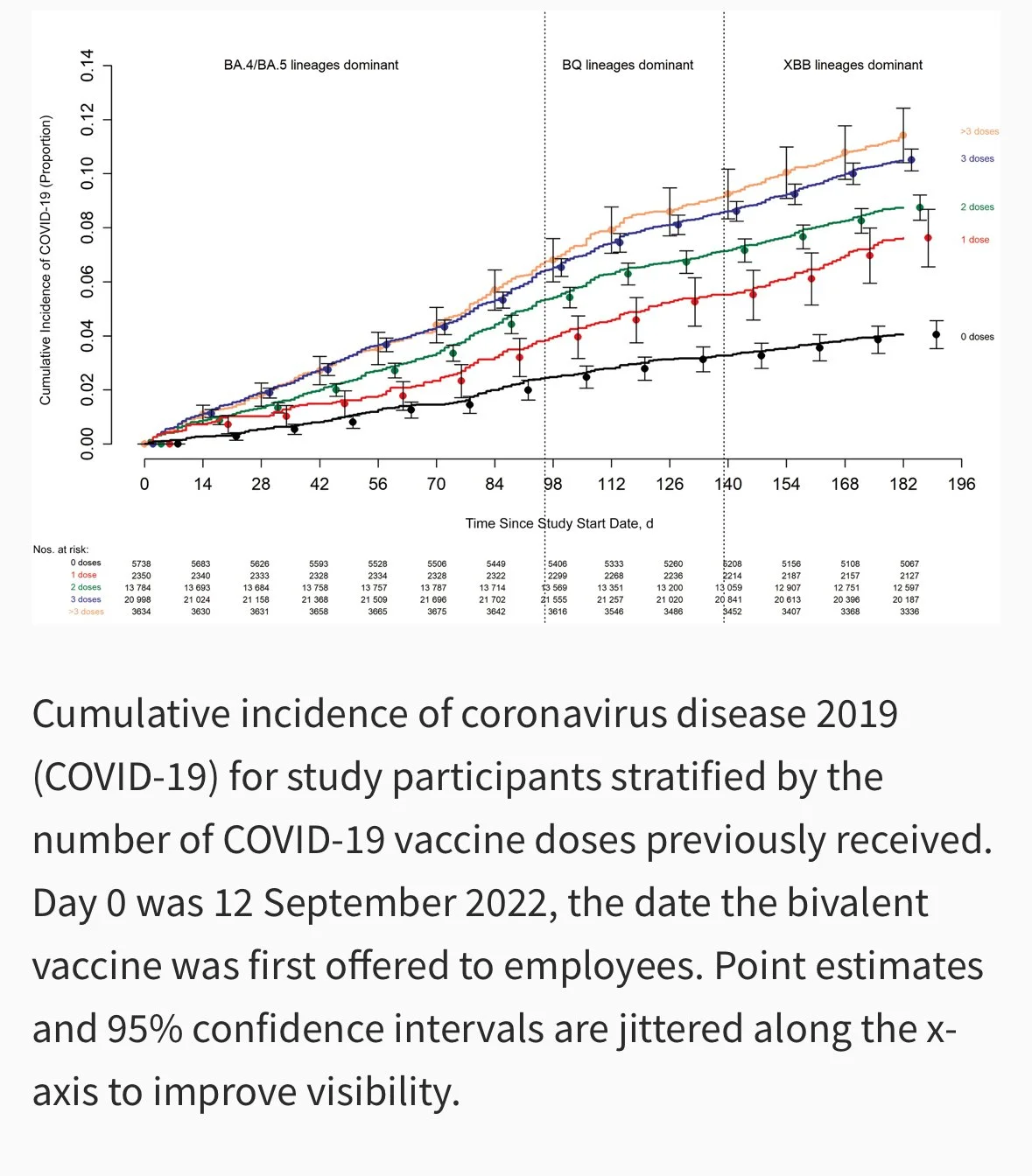
Immune imprinting and ADEI may partially explain the Cleveland Clinic publication which showed an increased rate of CoVID-19 infections that was strikingly correlated with a greater number of CoVID-19 vaccine doses. See the graph below provided courtesy of Shrestha et al of Cleveland Clinic:
Source Shresthra et al
Fortunately despite the increased rate of infections, these have been mostly mild to date. This is due to a number of factors.
Firstly, Omicron had a lower tendency to cause severe disease compared to the Delta variant.
Secondly, the sub-optimal antibody response has two opposing effects: while opening the door to infection, at the same time, they have also protected against severe infection by a separate mechanism which protects air exchange cells in the lower lungs and cells in other organs from fusing. This fusogenic effect was the factor that made Delta so dangerous. Even though the more recent strains have actually become more fusogenic (virulent), they are still being blocked by these antibodies.
However there is a real risk that a virulent strain may be able to escape the protection currently offered by these antibodies via a chance mutation. If this occurs and the innate immune system hasn’t been constantly trained and updated, the consequences could be severe.
An additional concern is that any dominant strain is highly likely to retain the features which enable antibodies to speed up its entry into the cells, because any virus which loses this ability would not be able to compete and would be quickly eliminated from the race.
So in this scenario, instead of antibody dependent enhancement of (mild) infection, there would be antibody dependent enhancement of severe disease - AND in the potentially disastrous context of an untrained and unprepared innate immune system.
In other words, the immune system would not only leave the door open but would facilitate infection of a virulent covid variant. It is thought that the combination of these factors could produce rapidly progressive, severe, life threatening disease.
Fortunately none of the dominant strains have overcome this protective barrier to date. However there are sporadic cases in whom the antibodies have reduced below a protective threshold. This may partially explain the recent surge in hospitalizations and deaths currently reported - well in advance of a winter surge.
POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS?
Boosting innate immune function is a key priority. Strategies for boosting the innate immune function and other pro-active measures are covered in the Covid Defense article. This article focuses on utilizing photodynamic therapy (PDT), photobiomodulation (PBM) and specific evidence based posrbiotics to boost the innate immune system in persons who are most at risk.
PDT AND THE INNATE IMMUNE RESPONSE
PDT involves a photosensitizing agent that, when exposed to a specific wavelength of light, produces reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can destroy cancer cells and a wide array of infections, including bacterial, fungal, and viral infections. Cancer cells, infected cells and microorganisms are much more susceptible to ROS than normal cells.
PDT appears to have at least 3 beneficial effects which facilitates better functioning and training of the innate immune response.
Firstly, PDT can reduce the viral load by rapidly destroying viruses within seconds.
Secondly, destruction of viral laden cells provides a robust stimulus which increases both the number and effectiveness of innate immune cells. In this way photodynamic therapy lends a helping hand in clearing infection and reduces the likelihood of the innate system being overwhelmed.
Thirdly, there is evidence that activation of innate cells leads to a re-programming (ie training) which makes the innate system more capable of responding to any other infection, especially infection with a related pathogen.
Furthermore, there is evidence that innate immune training is significantly augmented by repeated treatment sessions leading to “…a broad innate immune activation…”
Click here for more scientific detail
PBM AND THE INNATE IMMUNE RESPONSE
Photobiomodulation (PBM) refers to the use of light to stimulate biological processes. While traditionally used for wound healing, pain reduction, and tissue repair, there is also evidence that PBM can enhance the innate immune response.
Like PDT, PBM has also been shown to significantly improve the function of innate immune cells and even optimizes the specialized receptors involved in the training of this system.
Very importantly there is substantial evidence PBM can activate and stimulate the production of immune cell precursors referred to as mesenchymal stem cells. These stem cells are generated within the bone marrow and elsewhere. It has also been suggested that PBM can counteract the reduced function of the thymus gland where lymphocytes mature and get ready for action. The activity of the thymus gland gradually decreases with age and is an important factor in susceptibility to infection.
Click here for more scientific detail
Postbiotics and the Innate Immune Response
The body has trillions of resident microbial species predominantly in the gut, which fundamentally impacts the health of all organ systems positively or negatively depending on the mix of microbes present. Postbiotics are bioactive compounds that are produced from probiotics (live bacteria). Unlike probiotics, which are live microorganisms, postbiotics are non-living products and therefore do not pose a risk to those with impaired immunity and avoids concerns about the viability of these microorganisms at the time they are administered.
Postbiotics provide a number of health benefits including reduced inflammation, resisting growth of harmful bacteria and reinforcing the integrity of the gut barrier (very important to prevent pathogens and toxins crossing from the gut into the bloodstream).
Postbiotics can also have a positive effect on glucose and lipid metabolism potentially counteracting obesity and type 2 diabetes - risk factors for severe CoVID-19 disease.
With regard to immune function, postbiotics have also been demonstrated to significantly improve immune response in the gut, the lungs and throughout the whole body. In particular the MCC1849 and L-137 postbiotic strains and the short chain fatty acids they produce are well supported by scientific evidence. Randomized clinical studies have shown a reduction in the rate and severity of viral infections with the use of these strains via a number of mechanisms:
Components of the inactivated bacterial strains provide a powerful stimulus to activate immune cells involved in the first line of defense against viruses and other types of infection via special pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs).
The production of interferon and other chemicals which are critically important for fighting viral infections is enhanced.
The immune response is balanced with the production of other chemicals which dampen the inflammation, thus avoiding a cytokine storm.
Cells which phagocytose (attack and engulf) viruses directly are stimulated.
Natural killer cells are signaled to spring into action to eliminate cells infected with viruses.
Click here for more scientific detail
THERAPEUTIC RATIONALE of the Luminnova p3 Protocol
The aim of therapy is to leverage the ability of PDT, PBM and postbiotics to boost the innate and an appropriate adaptive immune response to CoVID-19 infection in those at risk of severe disease:
Significantly increase the general readiness of the innate immune system to tackle infection
Capitalize on currently high CoVID-19 viral circulation as an opportunity to promote more specific training of the innate system targeted at future CoVID-19 strains as explained above.
For persons who experience acute CoVID-19 infections: reduce the negative effects by directly reducing viral load. This can offer protection from the recognized immunosuppressive effects of CoVID-19 infection including reduced lymphocyte counts.
Potentially shift the dominant (mismatched) imprinted immune response away from the original CoVID-19 strain and towards currently circulating variants.
Lessen the risk due to other types of infections as these measures have a very broad effect.
HOW CAN THIS BE ACHIEVED?
Sublingual PDT/PBM
Systemic PDT/PBM can be achieved by directing light therapy at appropriate wavelengths and power under the tongue (sublingually) thereby achieving a non-invasive, full body therapy. The light therapy is administered after giving an oral photosensitizer and timed to coincide with its peak absorption.
Patients sometimes report mild, transient myalgia (aching muscles) a few hours following the initial PDT/PBM sessions which appears to be related to activation of the innate immune response. In our experience, these treatments have resulted in expedited recovery of severe CoVID-19 disease, documented eradication of reactivated viruses like cytomegalovirus and significant clinical improvement in Lyme disease.
PBM Sternum
Treatment over the sternum bone in the chest has been recommended as a means of targeting both the thymus gland and the mesenchymal stem cells.
Home Based Treatments
These treatments have traditionally been offered at medical facilities. However, Luminnova Health has designed a home based devices so those most at risk can self-administer sublingual and sternum treatments on a periodic basis to stimulate and maintain an augmented innate immune response, with the aim of reducing the risk of severe infection.
Postbiotic Formulation
Luminnova Health has selected Flora-Matrix Postbiotics as this product provides evidence based dosages of MCC-1849, L-137 and short chain fatty acids.
PLEASE NOTE:
It is important to emphasize that no guarantee can be made regarding the level of protection that can be afforded by taking these measures. Furthermore they should be carried out in conjunction with healthy lifestyle practices plus the use of other prophylactic measures where and when necessary (See Covid / Viral Defense).